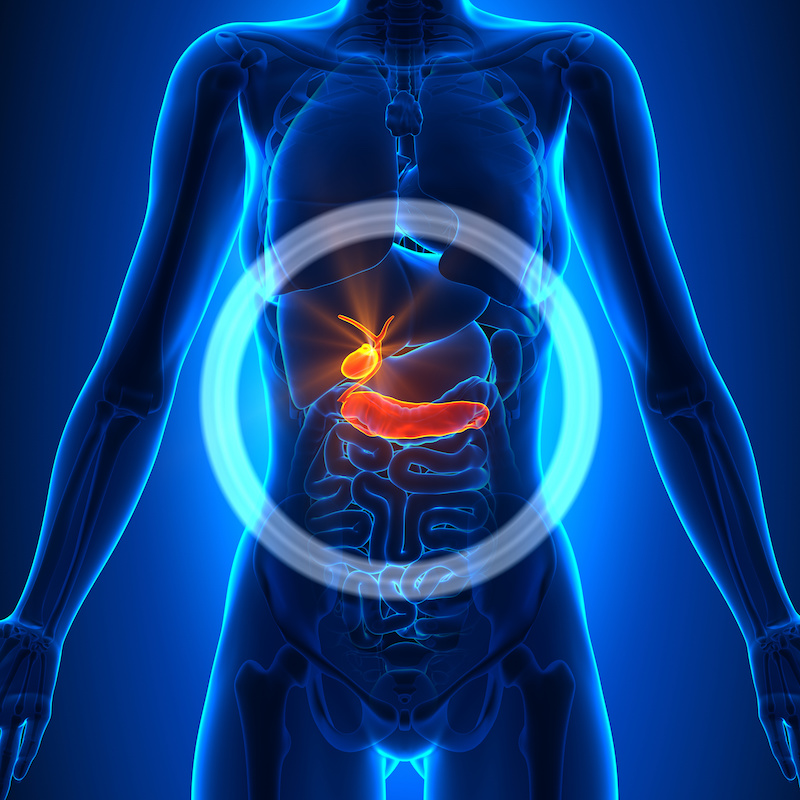
What is a Cholecystectomy
Cholecystectomies are one of the most over performed surgeries in the United States, and far too often, completely uncalled-for. Even in the presence of gallstones, one should always consider alternatives before rushing under the knife. The gallbladder is an essential organ responsible for collecting and storing bile in order to process and digest fats. To say that it can just be removed without consequence, is rather reckless. Aside from a number of potential dangers and complications stemming from its removal, weight problems and diabetes type two risks rise significantly.
Gallbladder attacks are often a sign of much larger problems, problems that do not simply disappear only once a small piece of that puzzle is removed. Our typical desire for instant gratification, coupled with the misconstrued notion that the gall bladder is an unnecessary organ, has led to an alarming number of these senseless surgeries.
Continue reading “The Gallbladder: Facts and Myths”
 Regular physical activity can offer us a multitude of health benefits. Recent studies show just 20 minutes a day can produce anti-inflammatory effects, adding to the already lengthy list of how fitness can support our bodies. That’s right! In addition to reducing heart disease, lowering
Regular physical activity can offer us a multitude of health benefits. Recent studies show just 20 minutes a day can produce anti-inflammatory effects, adding to the already lengthy list of how fitness can support our bodies. That’s right! In addition to reducing heart disease, lowering  Science has determined that chronic inflammation plays a role in many diseases, including those that are commonly understood as inflammatory diseases as well as others that were not originally connected with inflammation, such as obesity and
Science has determined that chronic inflammation plays a role in many diseases, including those that are commonly understood as inflammatory diseases as well as others that were not originally connected with inflammation, such as obesity and